Learning Objectives
By the end of this chapter, you will be able to:
- Identify and describe the 8 key elements of a business model.
- Identify and describe the major B2C business models.
- Identify and describe the major B2B business models.
- Understand how these models are being applied by e-commerce businesses in Nepal.
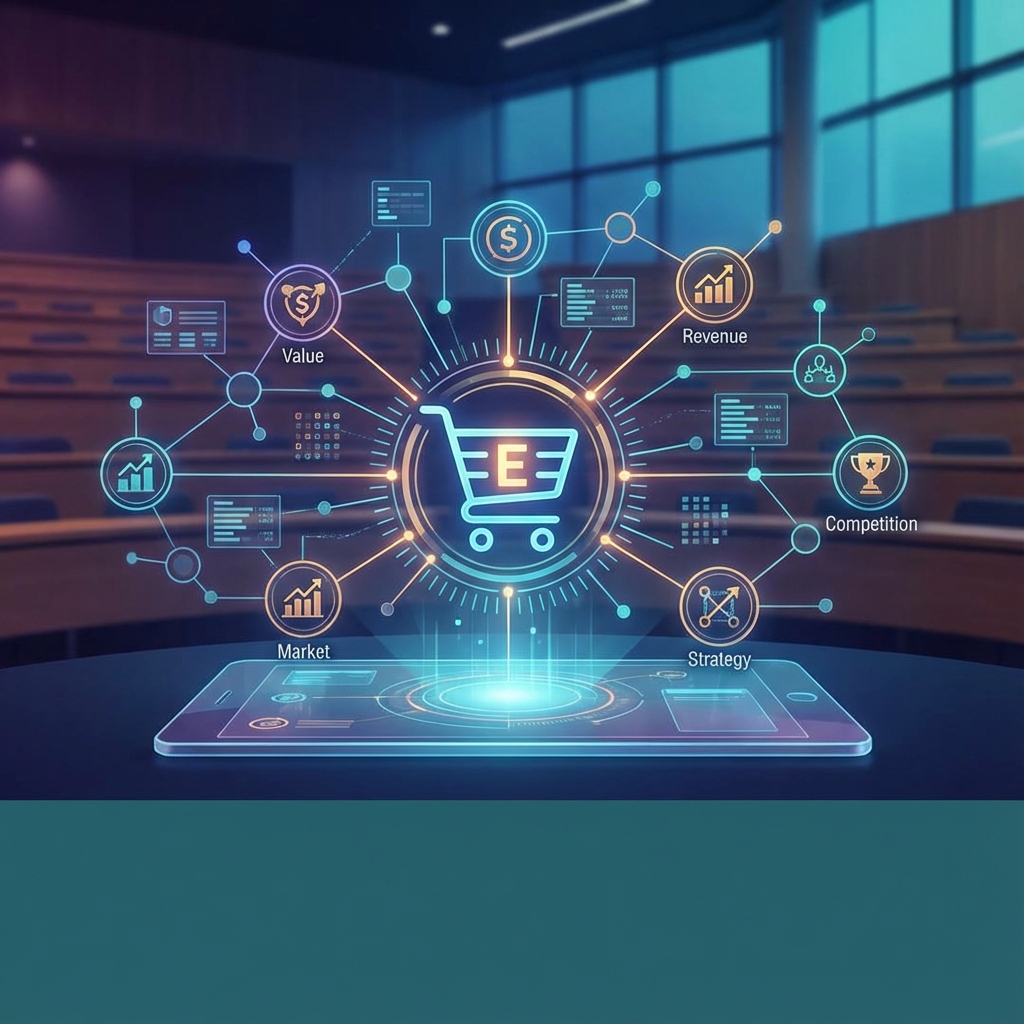
8 Key Elements of a Business Model
A business model is a set of planned activities designed to result in a profit in a marketplace. There are 8 key elements to a business model:
- Value Proposition: How a company’s product or service fulfills the needs of customers.
- Revenue Model: How the firm will earn revenue and produce profits. Common models include advertising, subscription, transaction fee, sales, and affiliate models.
- Market Opportunity: The marketspace a company intends to serve and its overall potential financial opportunities.
- Competitive Environment: The other companies operating in the same marketspace with similar products.
- Competitive Advantage: How a firm can produce a superior product or bring it to market at a lower price than competitors.
- Market Strategy: The plan for how to enter a new market and attract new customers.
- Organizational Development: The plan for how the company will organize its work.
- Management Team: The people responsible for making the business model work.
Major B2C Business Models
- E-tailer: Online retail stores. Example: Amazon, and in Nepal, Daraz and Sastodeal.
- Community Provider: Creates an online environment for people with similar interests to connect and transact. Example: Facebook, Instagram.
- Content Provider: Distributes digital content like news, music, and video. Example: Netflix, and in Nepal, Onlinekhabar and Hamro Patro.
- Portal: Offers powerful web search tools plus an integrated package of content and services. Example: Google, Yahoo.
- Transaction Broker: Processes online transactions for consumers. Example: Expedia, E*TRADE.
- Market Creator: Builds a digital environment where buyers and sellers can meet. Example: eBay, and in Nepal, Hamrobazar.
- Service Provider: Provides online services, from web storage to services performed offline. Example: Google Workspace, and in Nepal, food delivery services like Foodmandu and ride-sharing services like Tootle and Pathao.
Major B2B Business Models
- E-distributor: Companies that supply products and services directly to individual businesses. Example: Grainger. In Nepal, there are a number of e-distributors for office and industrial supplies.
- E-procurement: Companies that create and sell access to digital markets. Example: Ariba. In Nepal, Aayo is a B2B platform connecting manufacturers with retailers.
- Exchange: Independent digital marketplaces where hundreds of suppliers meet a smaller number of large commercial purchasers.
- Industry Consortium: Industry-owned vertical markets that serve specific industries.
Summary
A successful e-commerce business model is built on eight key elements, from value proposition to management team. These models are applied in both the B2C and B2B sectors. B2C models like e-tailers and content providers are common in Nepal, with local examples like Daraz and Onlinekhabar. The B2B sector, while still developing, is seeing growth with platforms like Aayo connecting businesses.
Key Takeaways
- A business model outlines how a company will be profitable, based on 8 key elements.
- Major B2C models include E-tailer, Content Provider, and Market Creator.
- Major B2B models include E-distributor and E-procurement platforms.
- The Nepali e-commerce landscape includes a variety of these models.
Discussion Questions
- What is the business model of Foodmandu? Which category does it fall into?
- How can a small e-commerce business in Nepal gain a competitive advantage against a large player like Daraz?
- What are the key differences between a B2C e-tailer and a B2B e-distributor?