Unit 8.5
Private B2B Networks
IT 204: E-Commerce
Learning Objectives
By the end of this chapter, you will be able to:
- ✅ Define what a private B2B network is and its core function.
- ✅ Identify the key benefits of implementing a private B2B network.
- ✅ Explain the concept of collaborative commerce and its role in B2B.
- ✅ Analyze the challenges and opportunities for private B2B networks in Nepal.
What is a Private B2B Network?
Definition: An online network, often called a private industrial network or private trading exchange (PTX), used by a single, large company to connect with its pre-approved suppliers, distributors, and other business partners.
🎯 Think of it as a "walled garden" for a company's most important business relationships, not a public marketplace.
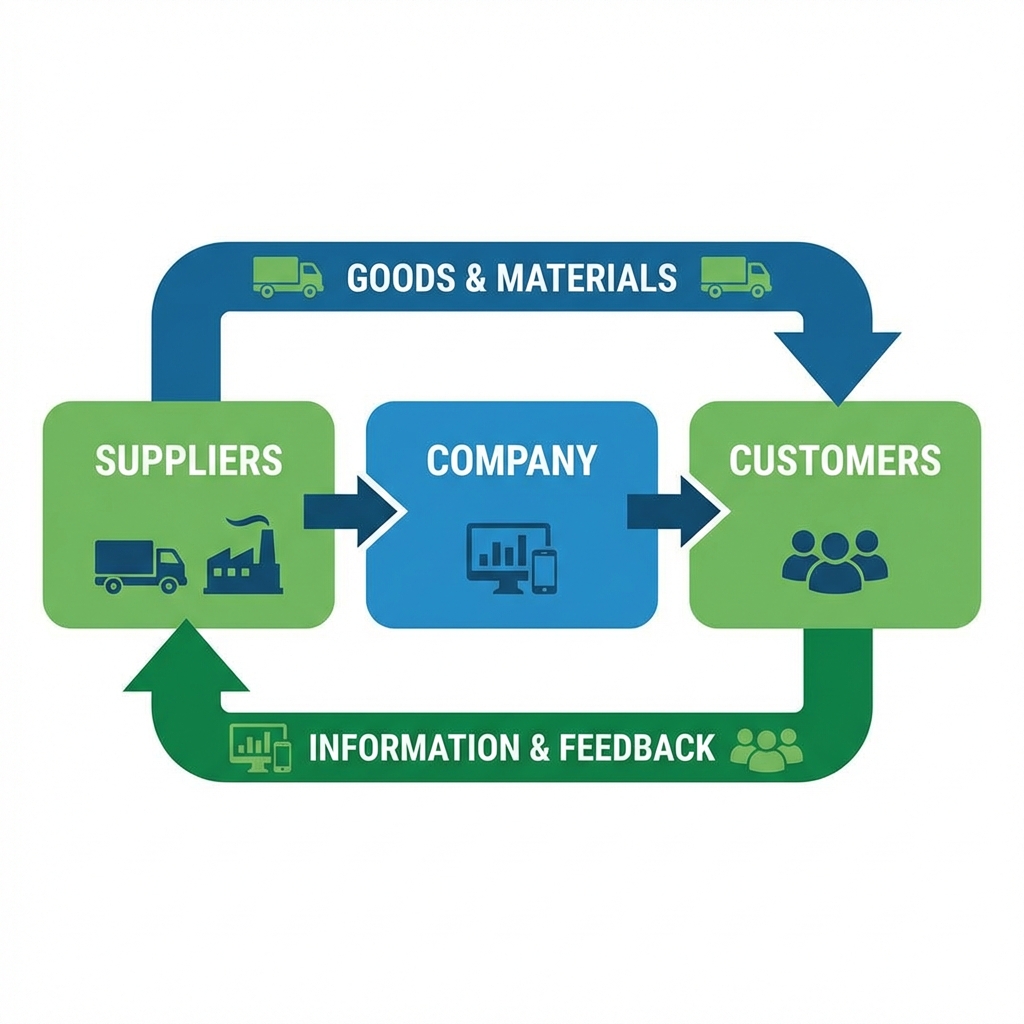
How It Works: The Core Loop
A single "host" company builds and manages the network.
⬇️
Selected suppliers and customers are given secure access.
All parties can share data, manage transactions, and collaborate on projects in a centralized, secure environment.
⬇️
This creates a highly efficient supply chain and communication channel.
Key Benefit 1: Improved Communication ⚡
- Centralized Hub: Provides a single source of truth for all partners. No more lost emails or version control issues.
- Real-time Information Sharing: Instantly share updates on inventory levels, production schedules, and shipping statuses.
- Direct Collaboration: Enables direct communication between relevant departments (e.g., engineering teams at the host and supplier company).
Key Benefit 2: Increased Efficiency 📊
Task Automation
- Automates routine processes like purchase orders, invoicing, and payment processing.
- Reduces manual data entry and human error.
Streamlined Operations
- Provides real-time visibility into the entire supply chain.
- Allows for faster decision-making and problem-solving.
Key Benefit 3: Reduced Costs 💰
By streamlining processes and improving efficiency, private B2B networks directly impact the bottom line.
- Lower Transaction Costs: Reduces the administrative overhead of managing B2B relationships.
- Optimized Inventory: Better demand forecasting leads to reduced need for "just-in-case" safety stock.
- Reduced Paperwork: Digitizes documents, saving on printing, postage, and physical storage costs.
The Role of Collaborative Commerce
Collaborative Commerce (c-commerce): The use of digital technologies to enable companies to collaboratively plan, design, develop, manage, and research products, services, and innovative e-commerce applications.
Private B2B networks are the primary platform where collaborative commerce happens.
- It's not just about buying and selling (transactions).
- It's about working together on shared goals (collaboration).
Case Study: Private B2B Networks in Nepal
While not yet widespread, the potential for growth in Nepal is significant. Let's examine the landscape.
🔍 Current Challenges in Nepal
Lack of Awareness
Many businesses are unfamiliar with the concept and its strategic benefits.
Skilled Personnel Gap
A shortage of IT professionals with experience in implementing and managing such networks.
Regulatory Framework
The legal and regulatory environment for complex e-commerce is still developing.
📈 Major Opportunities in Nepal
Growing SMEs
The backbone of the economy is actively seeking tools for efficiency and market access.
Government Support
The government is actively promoting e-commerce and digital transformation.
Affordable Tech
Cloud computing and mobile tech make these networks more accessible than ever before.
Practical Application
Example: A Nepali Handicraft Exporter
Imagine a large handicraft exporter in Kathmandu, "Himalayan Arts".
- They create a private B2B network to connect with their 50+ artisan groups across Nepal and their 10 major international buyers.
- Artisans can: See new orders in real-time, update production status, and manage raw material requests.
- Buyers can: Track their order progress from production to shipping, collaborate on new designs, and manage payments securely.
- Result: Faster production, fewer errors, and stronger relationships with both suppliers and customers.
Summary: Key Takeaways
- Private B2B networks are secure, invitation-only platforms for a company and its key partners.
- They drive major benefits in communication, efficiency, and cost reduction.
- These networks are the foundation for true collaborative commerce, moving beyond simple transactions.
- In Nepal, despite current challenges, the rise of SMEs and supportive trends create a fertile ground for future growth.
Thank You
Any questions?
Next Topic: Public B2B Exchanges & Marketplaces
Back to Start