Unit 6.case
Case Study: Instagram-First Fashion Brand in Kathmandu
IT 204: E-Commerce

Learning Objectives
By the end of this case study, you will be able to analyze how a startup leveraged social, mobile, and local marketing principles to build a successful e-commerce brand from the ground up.
- ✅ Analyze the "Instagram-First" direct-to-consumer (D2C) model.
- ✅ Deconstruct the key growth loops used in social commerce.
- ✅ Connect the brand's tactics to core concepts from Unit 6.
- ✅ Evaluate the strategic evolution from manual processes to scalable e-commerce infrastructure.

The Genesis: An Instagram-First Launch
This Kathmandu-based apparel brand bypassed traditional websites, launching directly where their target audience lived: Instagram.
Initial Strategy Breakdown
- 🎯 Primary Channel: Instagram feed, stories, and reels.
- 📢 Marketing Engine: Collaboration with local micro-influencers and encouraging User-Generated Content (UGC).
- 🛒 Sales Mechanism: Direct Message (DM) to place orders.
- 💰 Payment Method: Cash-on-Delivery (COD), a trusted method in the local market.
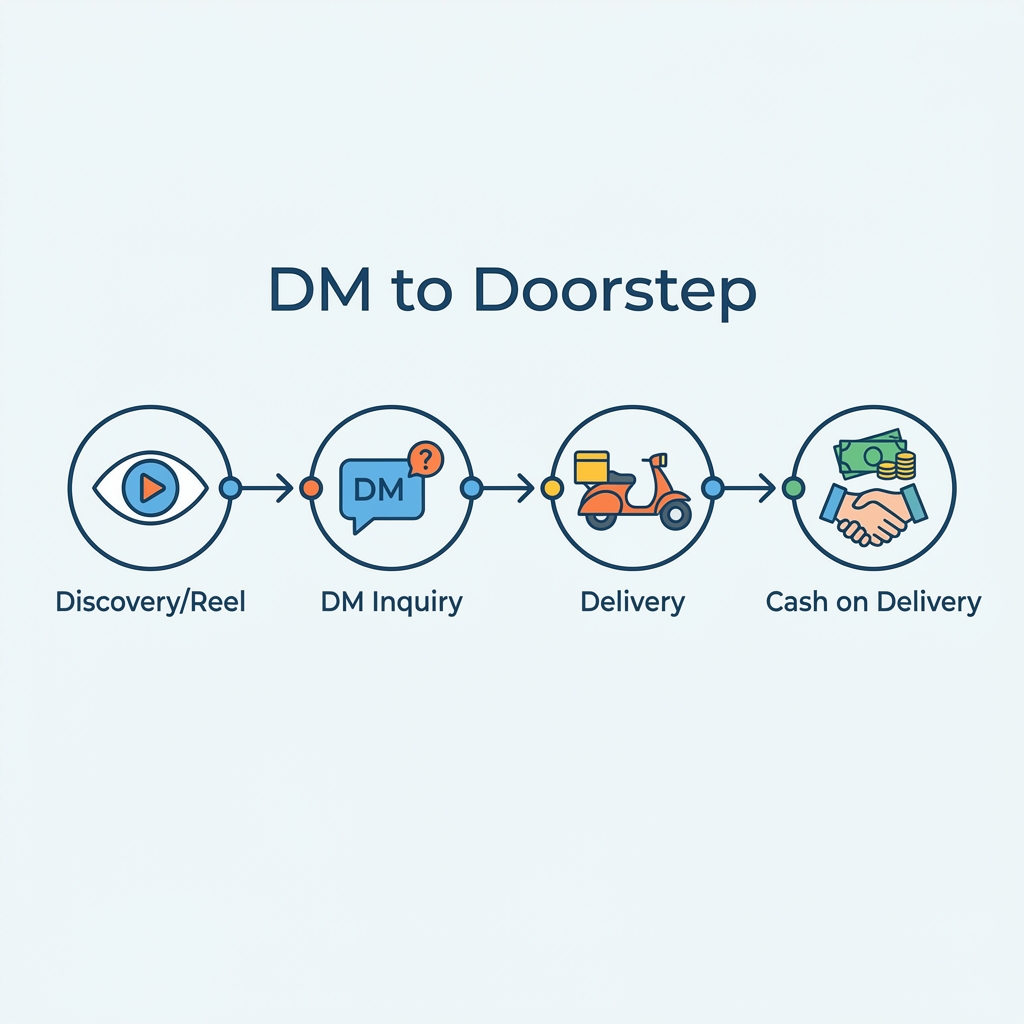
The Initial Funnel: DM-to-COD
The initial customer journey was simple, manual, and highly conversational, building trust with every interaction.
Customer Journey 🚶♀️
- Discovery: Sees a new "drop" in a Reel or creator post.
- Inquiry: Sends a DM asking for size, price, and availability.
- Order: Confirms order and provides delivery address in the chat.
- Payment: Pays cash to the delivery rider upon receipt.
Business Process ⚙️
- Monitoring: Manually tracks all incoming DMs for orders.
- Logistics: Coordinates with a local delivery service (e.g., Pathao).
- Fulfillment: Packages the order and hands it off for delivery.
- Reconciliation: Manually tracks payments received via COD.
Key Insight: This "scrappy" approach minimized initial tech costs and built a strong community, but was not scalable for high volume.
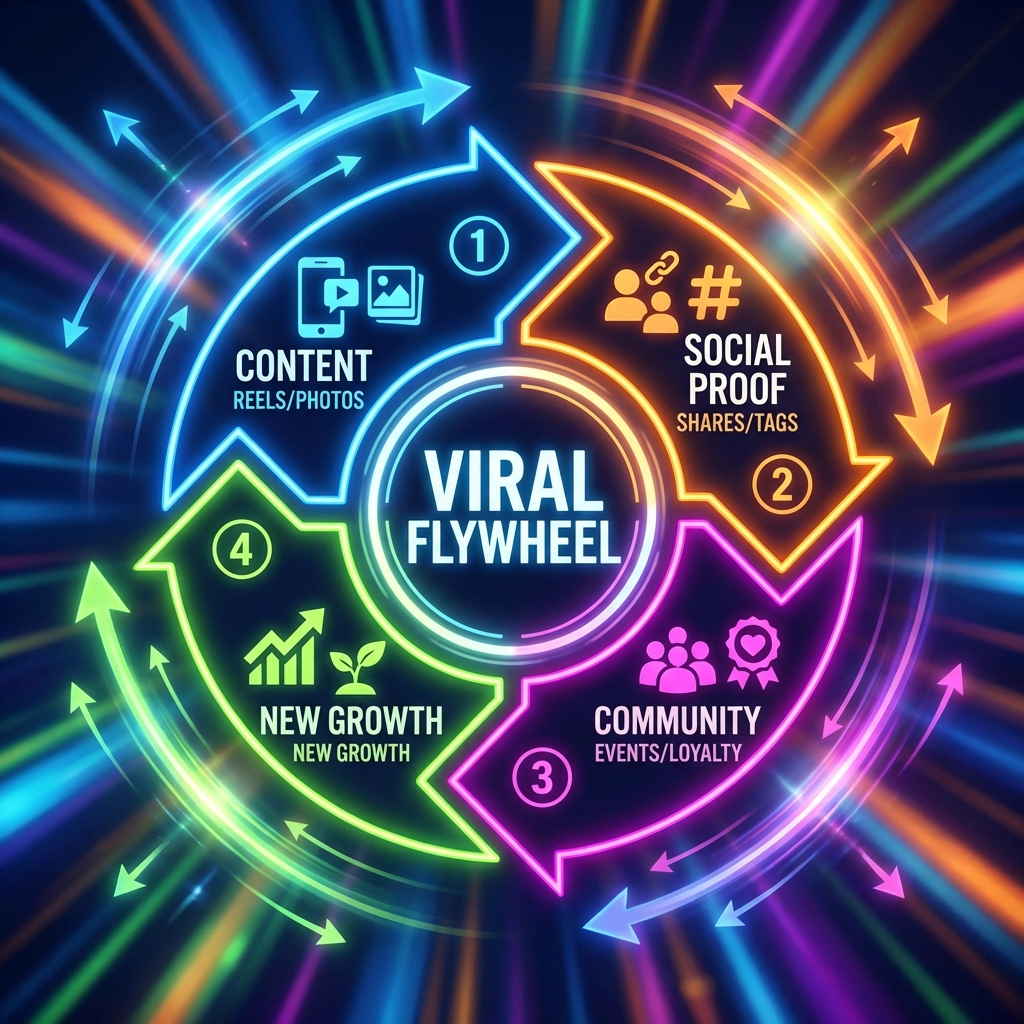
Building Growth Loops ⚡
The brand didn't just acquire customers; it built a self-reinforcing system to attract and retain them.
1. Content & Hype
- Weekly Drops: Creates urgency and repeat visits.
- Try-On Reels: Shows product fit and styling, reducing purchase anxiety.
2. Social Proof & Reach
- Creator Seeding: Provides authentic reach via trusted micro-influencers.
- UGC Highlights: Features customer photos, turning buyers into advocates.
3. Community & Exclusivity
- Pop-Up Events: Local try-on events to bridge the online-offline gap.
- VIP WhatsApp Groups: Offers early access and exclusive deals to top customers.
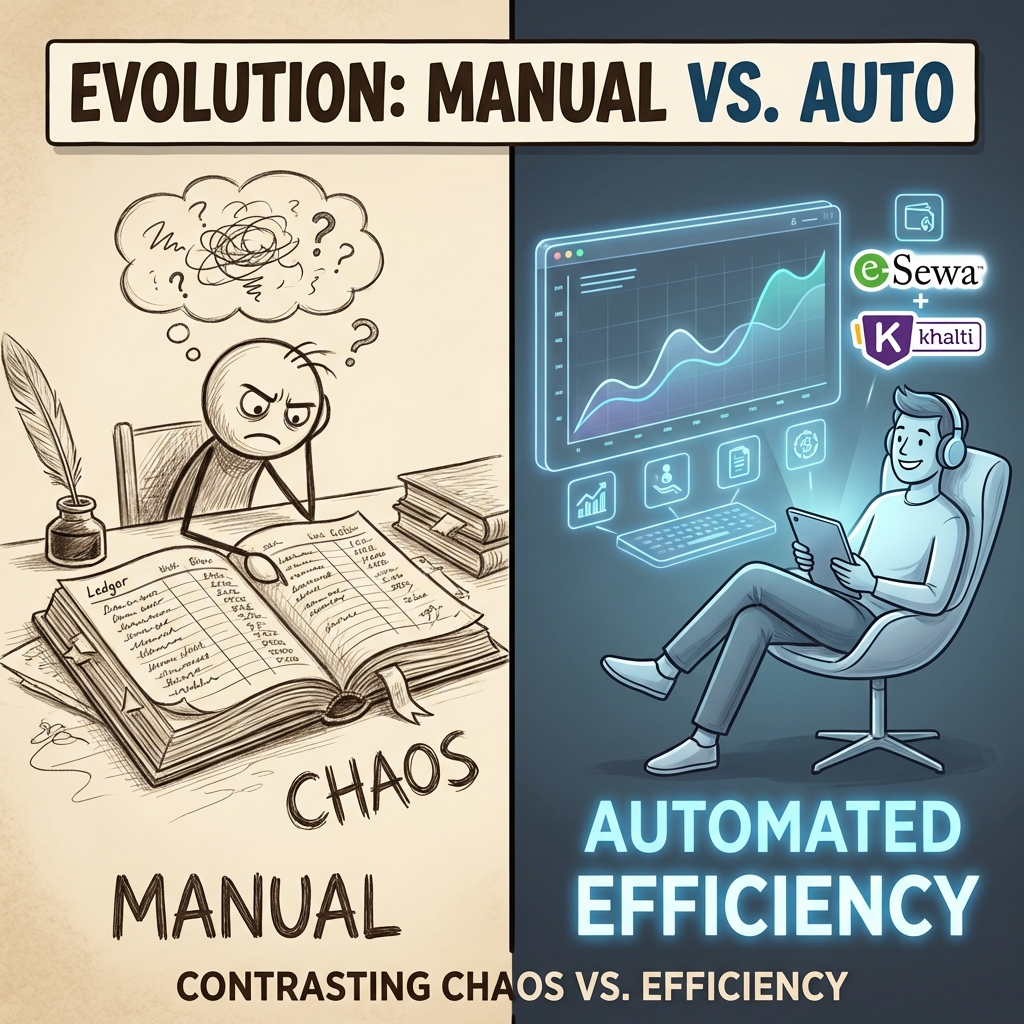
Evolution: From Manual to Automated
As order volume grew, the brand graduated from manual DMs to a more streamlined, scalable system.
Phase 1: Manual DM Flow
- Manual size/quantity checks
- Copy/paste address capture
- Prone to human error
- Time-consuming
- Limited to COD
Phase 2: Hybrid/Automated Flow
- DM automation for initial queries
- "Link-in-bio" to a simple checkout page
- Integrated digital payments (eSewa, Khalti)
- Better data tracking and inventory sync
- Frees up staff for customer service
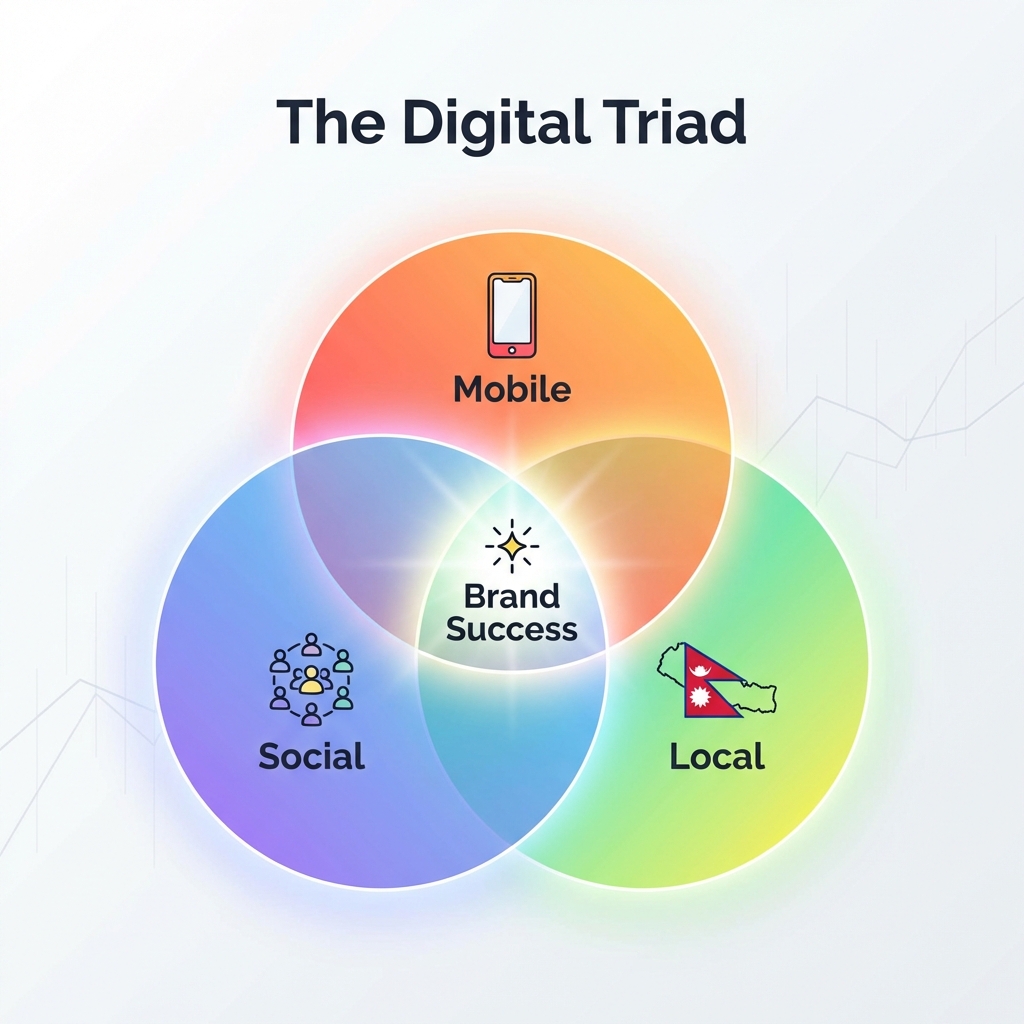
Connecting to Unit 6 Theory
This case study is a practical application of the core principles of social, mobile, and local marketing.
Social Marketing (6.1): The focus on community building, UGC, and creator seeding over traditional advertising demonstrates a strong understanding of social commerce dynamics. Community > Impressions.
Mobile Marketing (6.2): The entire funnel—from discovery on the Instagram app to ordering via DM—was mobile-native. This meets customers where they are, on the devices they use most.
Local Marketing (6.3): The use of COD, pop-up events in Kathmandu, and local delivery partners shows a strategy tailored specifically to the geographic and cultural context of its market.

🔍 Outcomes & Impact
The Instagram-first strategy yielded significant, measurable results in the brand's early stages.
Quantitative Wins 📊
- Rapid follower growth driven by viral reels and creator content.
- 35-45% of total sales were generated directly through Instagram DMs and links.
- Reduced dead inventory due to better demand forecasting from pre-orders on drops.
Qualitative Wins ✨
- Strong brand community and high customer loyalty.
- Direct line of communication with customers for instant feedback.
- High brand authenticity and trust within the local market.
Key Takeaways 🎯
The success of this Kathmandu brand provides several key lessons for modern e-commerce.
- Start Lean & Scrappy: You don't need a complex website to start selling. Validate your product-market fit using accessible tools like Instagram DMs.
- Community is Your Moat: An engaged community that creates UGC is a powerful, cost-effective marketing engine and a strong competitive advantage.
- Embrace Local Context: Success in e-commerce often depends on tailoring your strategy to local payment preferences (COD), logistics, and cultural norms.
- Evolve Your Tech Stack: Graduate from manual processes to automation and dedicated storefronts as your business grows and processes become bottlenecks.
Thank You
Next: Unit 7 - The Future of E-Commerce: AI and Personalization
Return to Course Home | Unit 6 Overview
IT 204: E-Commerce