Tools for Financial Data Analysis and Business Analytics
Unit 6.4: Using Computer Tools for Business Scenarios
IT for Business Course
Learning Objectives
By the end of this session, you will be able to:
- Identify key IT tools used for financial analysis in business.
- Explain the advanced features of spreadsheets (Excel, Google Sheets) for financial modeling.
- Describe the role of Business Analytics platforms like Power BI and Tableau.
- Recognize how tools automate the calculation and visualization of financial KPIs.
- Relate these tools to real-world business examples in Nepal.
Why Financial Analysis Matters
Financial analysis is the process of evaluating a business's performance and financial health to make better economic decisions.
- Profitability: Is the business making money?
- Liquidity: Can it pay its short-term bills?
- Efficiency: How well does it use its assets?
- Solvency: Can it meet long-term obligations?
The Role of IT Tools:
- Automation: Reduces manual calculation errors.
- Accuracy: Ensures data integrity from a single source of truth.
- Visualization: Turns complex numbers into easy-to-understand charts.
- Scalability: Handles large volumes of financial data effortlessly.
Spreadsheet Tools: The Foundation (MS Excel)
Excel remains a powerhouse for detailed financial modeling and analysis.
PivotTables
Quickly summarize large datasets. Perfect for analyzing revenue by product, region, or time period.
Financial Functions
NPV(): Net Present ValueIRR(): Internal Rate of ReturnPMT(): Loan PaymentsFV(): Future Value
These functions simplify complex investment and loan calculations.
What-If Analysis
Tools like Scenario Manager and Goal Seek help you forecast outcomes based on different variables.
Spreadsheets in Action: Collaboration & Templates
Google Sheets: Collaborative Modeling
Ideal for team-based financial planning.
- Real-time Collaboration: Multiple users can work on a budget simultaneously.
- Version History: Easily track changes and revert to previous versions.
- Cloud-Based: Access your financial models from anywhere.
Essential Financial Templates
Templates provide structure and save time.
- Cash Flow Statement
- Profit & Loss (P&L) Statement
- Budget vs. Actuals Tracker
- Balance Sheet
Business Analytics (BI) Platforms
BI tools connect to various data sources to create interactive and visually appealing financial dashboards.
Microsoft Power BI

Strong integration with the Microsoft ecosystem (Excel, Azure). Excellent for building comprehensive financial dashboards that can be shared across an organization.
Tableau

Known for its superior data visualization capabilities. Allows users to "drag-and-drop" to explore financial data and uncover trends intuitively.
Accounting & Enterprise Platforms
These systems are the primary source of financial data for analysis.
QuickBooks / Tally
The backbone for Small and Medium Enterprises (SMEs). They handle day-to-day accounting, invoicing, and generate standard financial reports like the Balance Sheet and P&L.
SAP FICO Module
An Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) solution for large corporations. It integrates Financial Accounting (FI) and Controlling (CO) to provide a complete picture of enterprise finances.
The Data Source
Data from these platforms is often exported to Excel or connected to BI tools for deeper, customized analysis and visualization.
Dashboard: Visualizing Financial KPIs
Dashboards consolidate Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) for a quick overview of financial health.
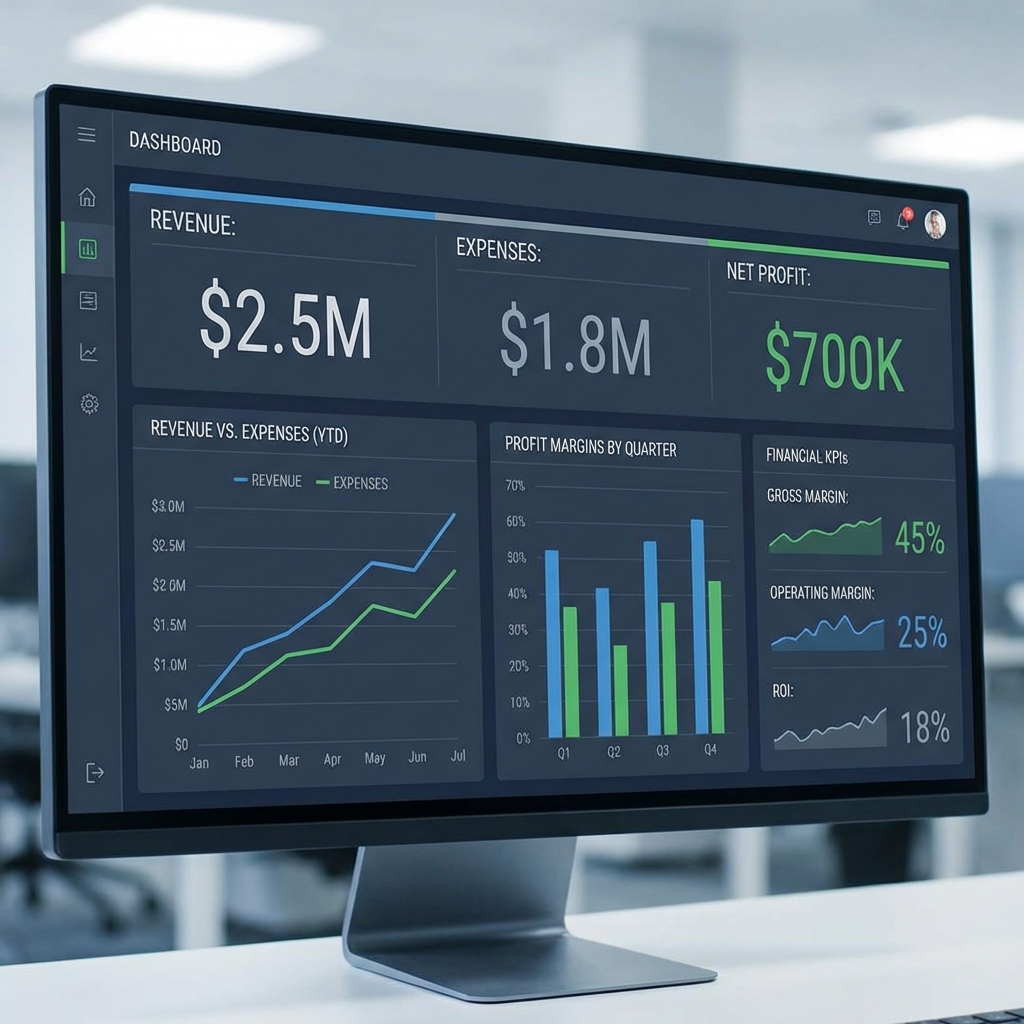
Tools in Action: Nepal Business Examples
Banking Sector
Nabil Bank uses advanced analytics and BI tools to assess credit risk. By analyzing customer transaction history and financial statements, they can build predictive models for loan default probability.
Manufacturing
CG Foods (Wai Wai) utilizes an ERP system like SAP to perform detailed cost analysis. This helps them monitor raw material prices, production efficiency, and supply chain costs to maintain profitability.
E-commerce & SMEs
Daraz analyzes sales data to optimize pricing and promotions. Meanwhile, thousands of Nepali SMEs rely on Tally for accounting, GST/VAT compliance, and generating financial reports.
Practical Applications in Business
How these tools support core financial activities:
-
Budgeting and Forecasting
Use Excel's Scenario Manager or Power BI to project future revenues and expenses under different economic conditions. -
Variance Analysis (Actual vs. Budget)
Create dashboards in Tableau or Power BI to visually compare actual spending against the budget, immediately highlighting areas of concern. -
Financial Scenario Planning
Model the financial impact of strategic decisions, such as launching a new product or entering a new market, using advanced spreadsheet models. -
Investor and Stakeholder Reporting
Generate professional, easy-to-understand financial reports and dashboards to communicate business performance effectively.
Key Takeaways
Spreadsheets are essential for detailed, flexible financial modeling and ad-hoc analysis.
BI platforms (Power BI, Tableau) transform raw financial data into interactive, visual stories for better decision-making.
Accounting/ERP systems (Tally, SAP) are the foundational source of truth for all financial data.
The right tool depends on the scale of the business and the complexity of the analysis required.
The ultimate goal is to generate actionable insights, not just reports.
Questions?
Thank You
Contact: your.email@university.edu.np