Deck 5.3
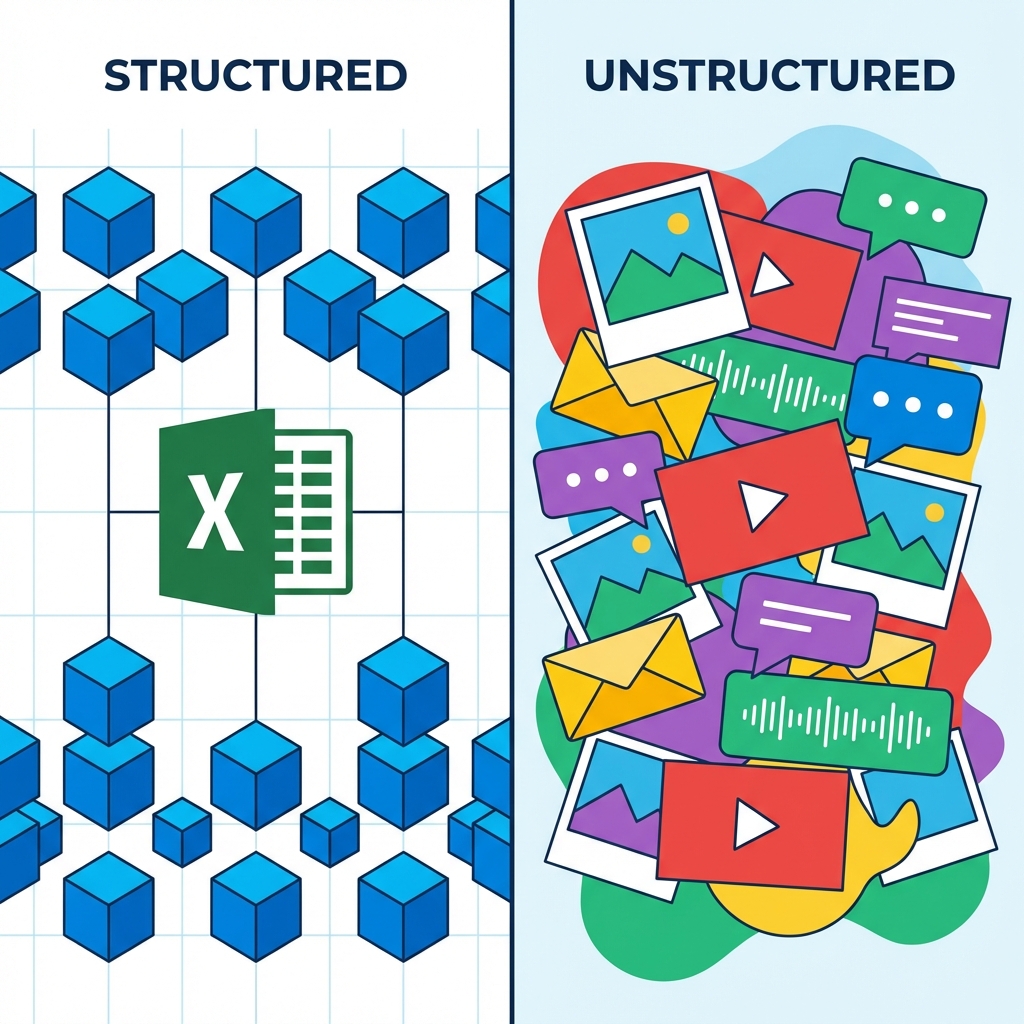
Types of Data: Structured vs. Unstructured
ICT 110: IT for Business
Today's Learning Objectives
By the end of this lecture, you will be able to understand the different types of data that fuel modern business decisions.
- ✅ Differentiate between raw data and business information.
- ✅ Relate structured and unstructured data types to specific business functions like Finance, HR, and Marketing.
- ✅ Define "Big Data" using the 3 V's (Volume, Velocity, Variety).
- ✅ Analyze how Nepali companies use different data types to gain a competitive advantage.
- ✅ Recognize the key ethical considerations in handling business data.
Data: The Lifeblood of Business
Data are raw, unorganized facts. When processed and given context, data becomes Information.
📊 Raw Data
101, "Laptop", 45, 85000
102, "Mouse", 150, 1200
💼 Business Information
We have 45 units of "Laptops" in stock, valued at NPR 3,825,000. This informs our inventory and financial planning.
Every business function, from accounting to marketing, runs on data.
Why Data Matters: A 360° View
Effective data management drives strategic decision-making across the entire organization.
- 💰 Finance: Accurate financial reporting, budgeting, and fraud detection.
- ⚙️ Operations: Supply chain optimization, inventory management, and quality control.
- 🤝 Human Resources: Payroll processing, performance tracking, and recruitment analysis.
- 🎯 Marketing: Customer segmentation, campaign analysis, and understanding customer needs.
What is Structured Data?
Highly organized data that fits neatly into a predefined model, typically tables with rows and columns. It is quantitative and easy to search and analyze.
Characteristics
- Pre-defined format (schema)
- Easy to enter, store, and query
- Examples: Numbers, dates, strings
Business Examples
- Financial transactions in an accounting system.
- Employee records in an HR database (Name, ID, Salary).
- Inventory levels in a warehouse system (Product ID, Quantity).
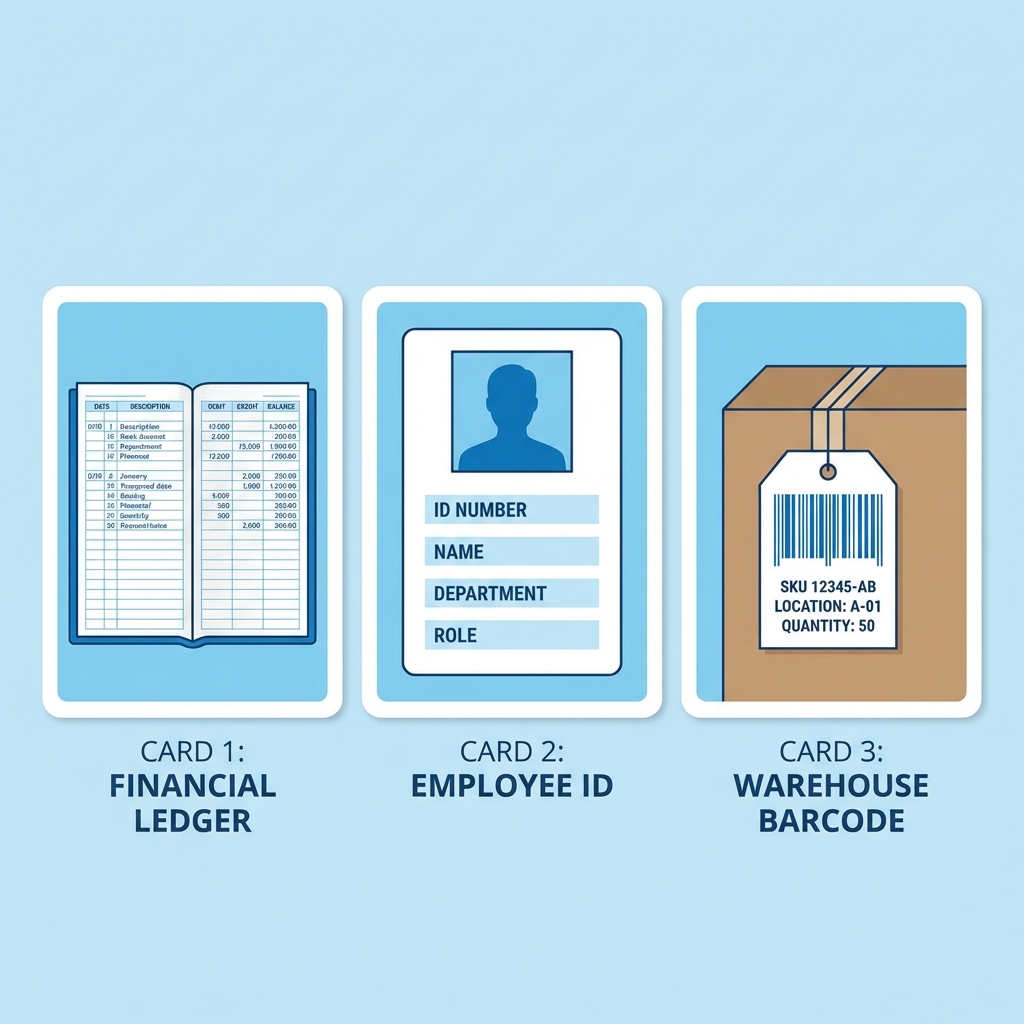
Structured Data in Action
This is the backbone of most core business operations.
💰 Finance: Ledger
| Date | Account | Debit | Credit |
|------------|---------|-------|--------|
| 2023-10-26 | Sales | | 50000 |
| 2023-10-26 | Cash | 50000 | |
🤝 HR: Employee Table
| Emp_ID | Name | Department |
|--------|-----------|------------|
| E101 | Anjali S. | Finance |
| E102 | Bikram R. | Operations |
⚙️ Operations: Inventory
| SKU | Item Name | Qty |
|--------|-----------|-----|
| LPT001 | Laptop | 45 |
| MSE003 | Mouse | 150 |
What is Unstructured Data?
Data that does not have a predefined format or organization. It is often qualitative, text-heavy, and contains rich insights but is harder to process.
Characteristics
- No pre-defined model
- Difficult to search and analyze with traditional tools
- Examples: Text, video, audio, images
Business Examples
- Customer emails or support chat logs.
- Minutes of a board meeting (Word document).
- CCTV footage for factory floor monitoring.
- Social media comments about a new product.
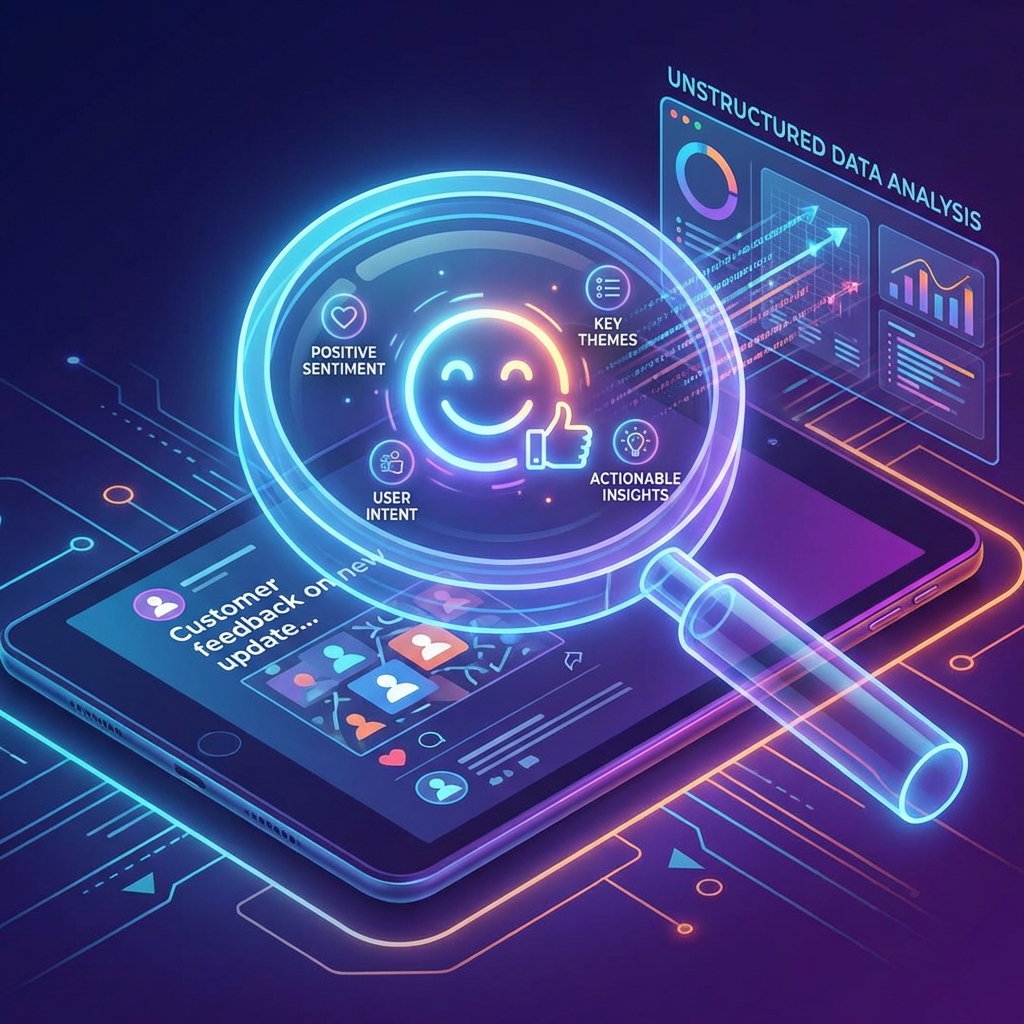
Unlocking Unstructured Data
Provides context and depth that numbers alone cannot.
🎯 Marketing/Service
Customer Email: "Hi, I received my order #1234 but the product was damaged. Can you please help me with a replacement? Thanks, Sita."
Insight: Potential issue in the shipping/packaging process (Operations). Poor customer experience (Service).
🤝 Human Resources
Performance Review Snippet: "Rajan has shown excellent leadership in the supply chain optimization project, but needs to improve his team communication skills."
Insight: Identifies a high-potential employee and a specific area for training and development.

Big Data: The 3 V's
Data that is too large or complex for traditional data-processing application software to adequately deal with.
Volume
The sheer scale of data. Think of the millions of daily transactions processed by a telecom company like Ncell or a digital wallet like Khalti.
Velocity
The incredible speed at which data is generated and must be processed. Think of real-time ride tracking in Pathao or live stock market data.
Variety
The different forms of data. Daraz collects structured sales data, unstructured text reviews, and image data for all its products.

Practical Application: Data in Nepal
Leading Nepali companies use data across all functions for a competitive edge.
eSewa (FinTech)
Manages vast volumes of structured data (transactions, user accounts) for financial reporting, fraud detection, and regulatory compliance. (Finance & Operations)
CG Foods (Manufacturing)
Leverages structured data from its ERP system to manage supply chain logistics, monitor production schedules, and forecast demand for products like Wai Wai. (Operations)
Daraz (E-commerce)
Blends structured data (sales, inventory) with unstructured data (customer reviews, search queries) to personalize recommendations and optimize stocking. (Marketing & Ops)
A Leading Bank (Finance)
Uses structured customer history for credit risk analysis (Finance) and unstructured data from call center logs to improve customer service training (HR/Service).
Ethical Considerations & Security
With great data comes great responsibility.
Data isn't just a business asset; it's often personal and sensitive information about customers and employees.
- Data Privacy: How are you collecting and using customer data? Is it transparent? (e.g., Khalti's privacy policy)
- Data Security: How are you protecting data from breaches? A breach can ruin a company's reputation and lead to huge financial loss.
- Bias in Data: Can your data create unfair outcomes? E.g., a loan approval algorithm that is biased against certain demographics.

Summary & Key Takeaways
- 🎯 Data is a core strategic asset, but it only becomes useful information when given context.
- 📊 Businesses rely on both structured data for core operations and unstructured data for deep insights.
- 🌪️ The era of Big Data (Volume, Velocity, Variety) requires new tools and strategies for analysis.
- 🇳🇵 Nepali companies are actively using both types of data to improve efficiency and customer experience.
- ⚖️ Effective data management is not just a technical challenge, but an ethical responsibility.
Thank You
Any questions?
Next Topic: Introduction to Data Management & DBMS