Unit 4: Computer Networks
Network Security: Firewalls, IPSec, and VPNs
ICT 110: IT for Business
Learning Objectives
- ✅ Explain the role of a firewall in protecting corporate data across all business functions.
- ✅ Describe how IPSec ensures secure transmission of sensitive financial and operational data.
- ✅ Analyze the business case for using VPNs to support remote work and inter-branch connectivity.
- ✅ Identify appropriate security solutions for common business scenarios.
Why Network Security Matters in Business
Data is a critical asset for every department. Protecting it is not just an IT job; it's a business necessity.
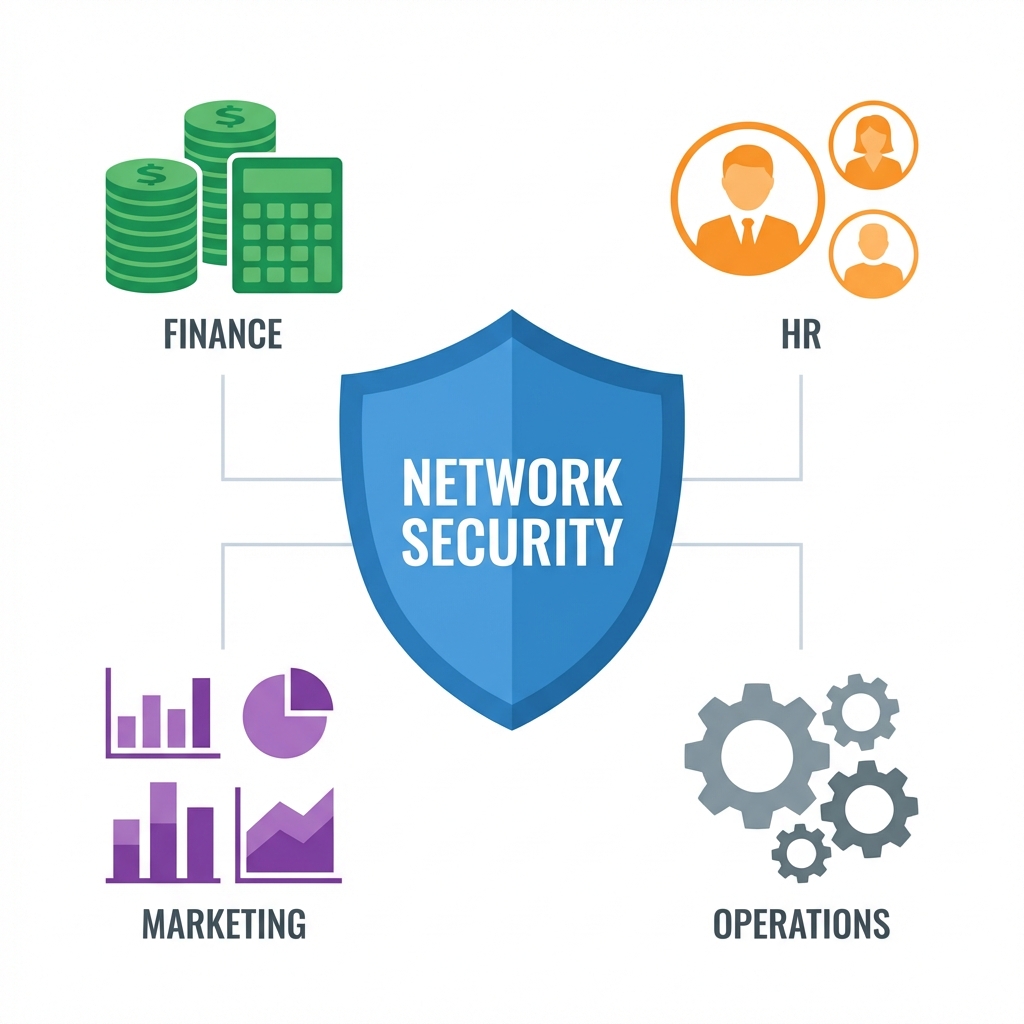
Protecting Core Assets 資産
- 💰 Finance: Financial statements, transaction records, payroll data.
- 🤝 HR: Employee personal information, salary details, performance reviews.
- 📊 Marketing: Customer lists, campaign strategies, market research data.
- ⚙️ Operations: Supply chain logistics, inventory levels, proprietary process data.
Mitigating Business Risks リスク
- Financial Loss
- Reputational Damage
- Operational Disruption
- Legal & Regulatory Penalties
Visualizing What We Protect
Topic 1: Firewalls - The Digital Gatekeeper
Think of it as the security guard at the entrance of your company's digital office building.
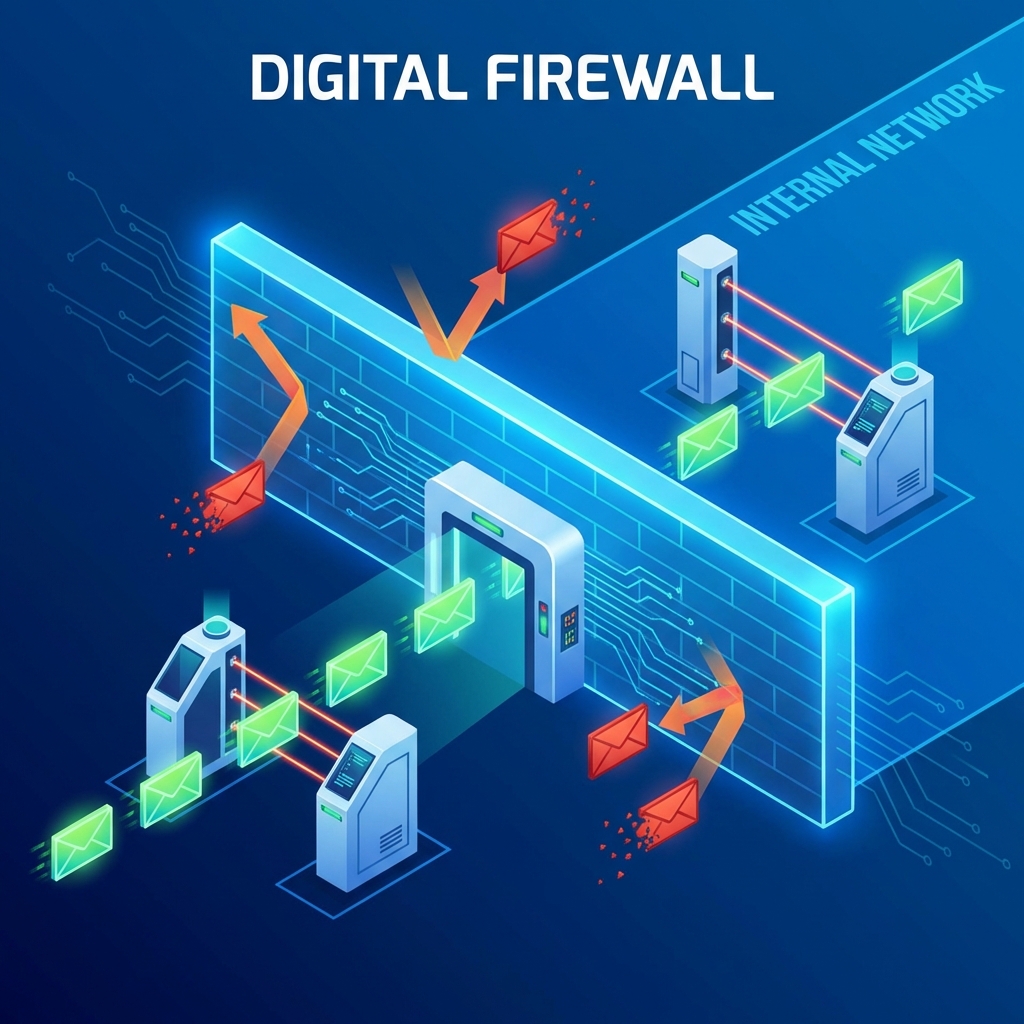
How Firewalls Protect Business Functions
Scenario: A typical company network
- 🛡️ Finance Dept: The firewall blocks all external attempts to access the internal accounting server, preventing fraud and data theft.
- 🛡️ HR Dept: It restricts access to the HR information system (HRIS), ensuring only authorized personnel can view sensitive employee data like salaries and NID numbers.
- 🛡️ Operations Dept: The firewall ensures that only traffic from trusted supply chain partners can reach the inventory management system, preventing disruption.
- 🛡️ Marketing Dept: It protects the Customer Relationship Management (CRM) database from being downloaded by competitors or hackers.
Transition: Protecting Data in Motion
Firewalls protect the perimeter (the "gate").
But what about data traveling between trusted locations over the public internet?
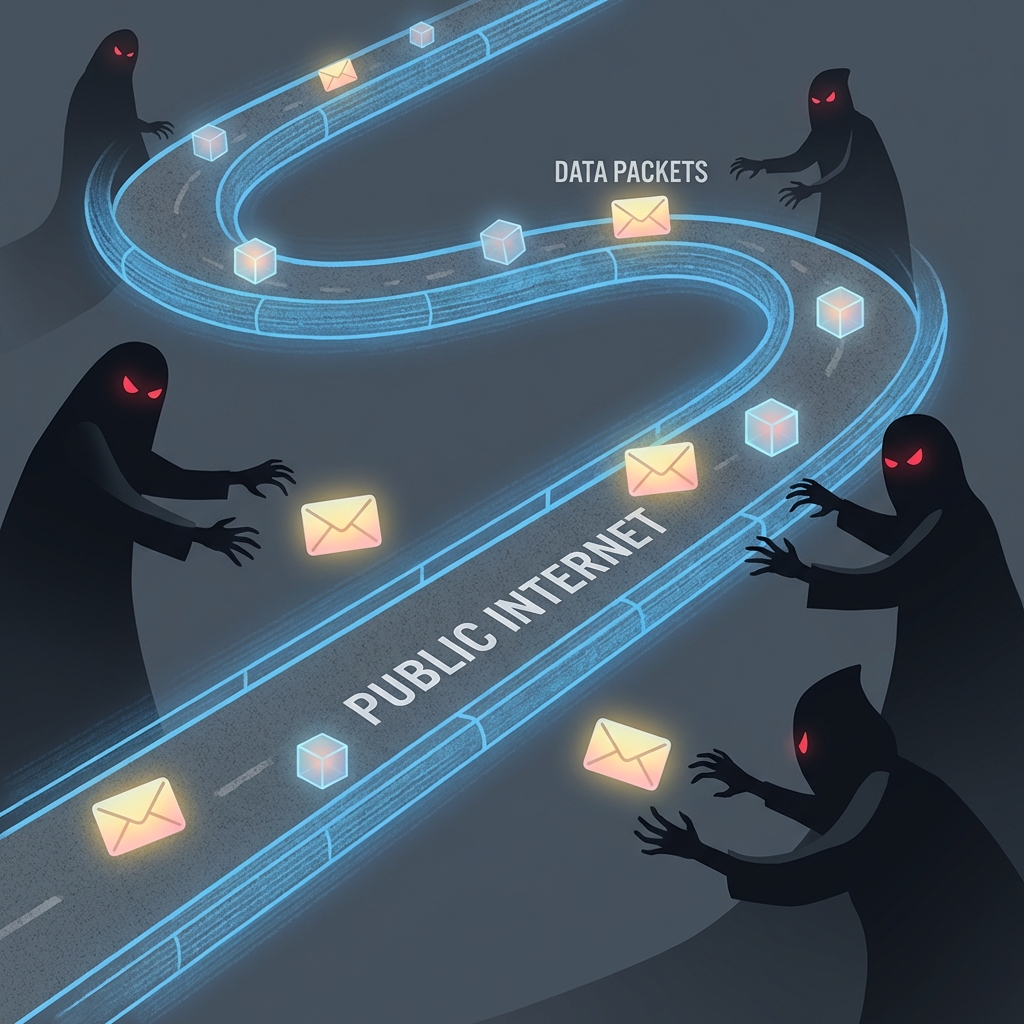
Example: The finance team at the head office in Kathmandu needs to send the quarterly budget to the branch office in Pokhara. How can we ensure this sensitive file is not intercepted and read by others on the internet?
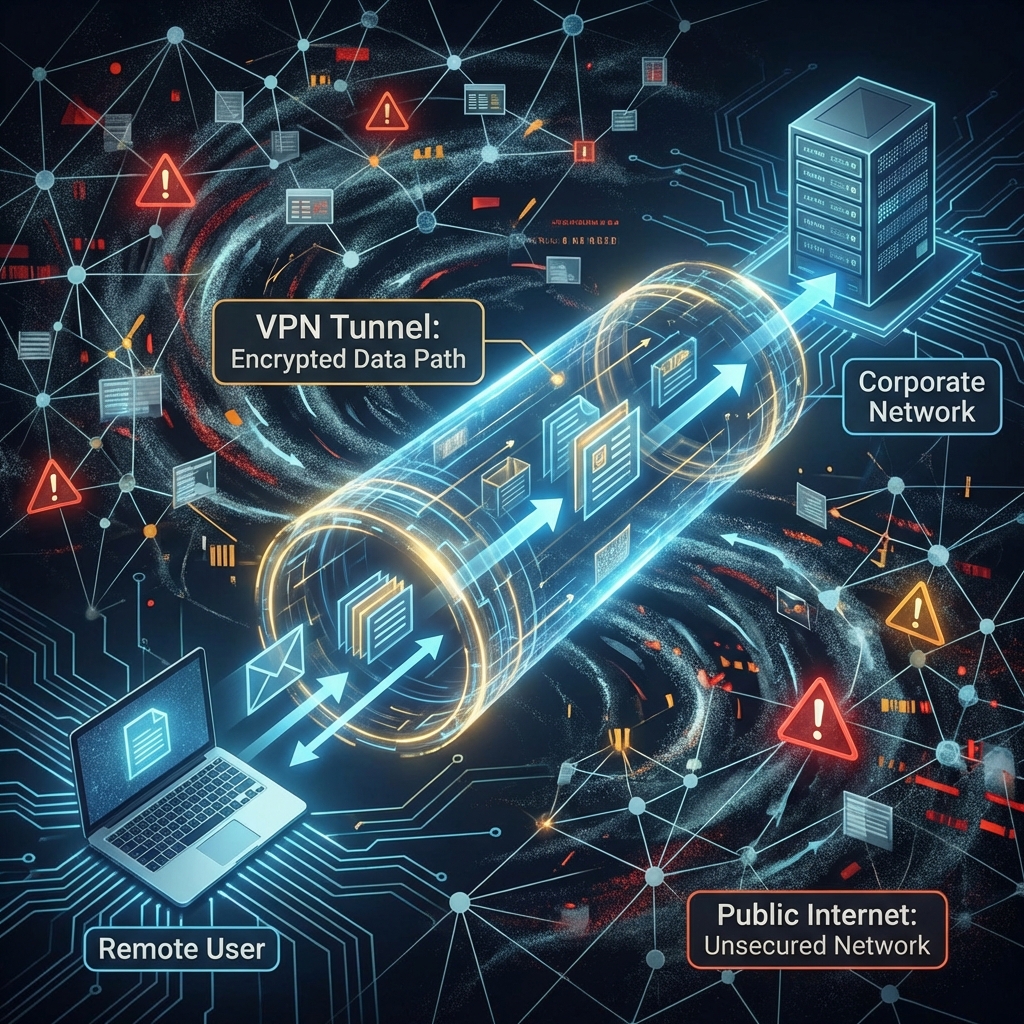
The Risk of Public Networks

Topic 2: IPSec - The Armored Truck for Data
Key Functions
- Authentication: Verifies that the data is from a trusted source. (Like checking an ID card)
- Encryption: Scrambles the data, making it unreadable to anyone without the correct key. (Like putting the data in an unbreakable safe)
Business Application
Primarily used for creating secure site-to-site connections between corporate offices, data centers, and trusted partners.
IPSec in Business Scenarios
⚙️ Operations & Supply Chain
A manufacturing company's factory in Birgunj securely and automatically transmits production data to the head office's ERP system in Kathmandu via an IPSec tunnel.
💰 Finance & Banking
A commercial bank uses IPSec to ensure that all transaction data communicated between its branches and its central data center is completely confidential and tamper-proof.
Transition: The Modern Workforce
The office is no longer just a physical building.
How do we provide secure access for employees working from home, traveling, or at client sites?
Challenge: An HR manager working from home needs to access the internal payroll system. A salesperson at a client's office needs to update the company CRM. How do they connect securely?
Topic 3: VPNs - The Secure Private Tunnel
Think of it as a secure, private subway line from your laptop directly into your company's office network, bypassing all public stops.
VPNs: Enabling Modern Business Agility
💼 Secure Remote Access
Empowers employees to work from anywhere. A project manager can access internal project files, or an accountant can run financial reports from home, all with the same level of security as being in the office.
🏢 Site-to-Site Connectivity
A cost-effective way to connect branch offices. A new retail store can be quickly and securely connected to the head office's inventory and sales systems using a site-to-site VPN.
🌍 Access Control
Allows businesses to control access to resources. A contractor can be given VPN access only to the specific server they need for their project, and nothing else, enhancing security.
Practical Application in Nepal
How Nepali Businesses Use These Technologies
- eSewa / Khalti (FinTech): Use powerful firewalls and encryption (like that in IPSec/VPNs) to protect every digital transaction and secure user financial data against cyber threats.
- Daraz (E-commerce): Relies on VPNs for its corporate employees to securely manage logistics, customer data, and seller portals from various locations, ensuring operational continuity.
- Chaudhary Group (Manufacturing): Uses site-to-site IPSec/VPNs to securely link its widespread factories and corporate offices, enabling real-time, secure sharing of production, inventory, and financial data.
- Commercial Banks (e.g., Nabil, NIC Asia): All banks use a combination of firewalls, IPSec, and VPNs to protect customer data, secure ATM networks, and enable secure inter-branch communication.
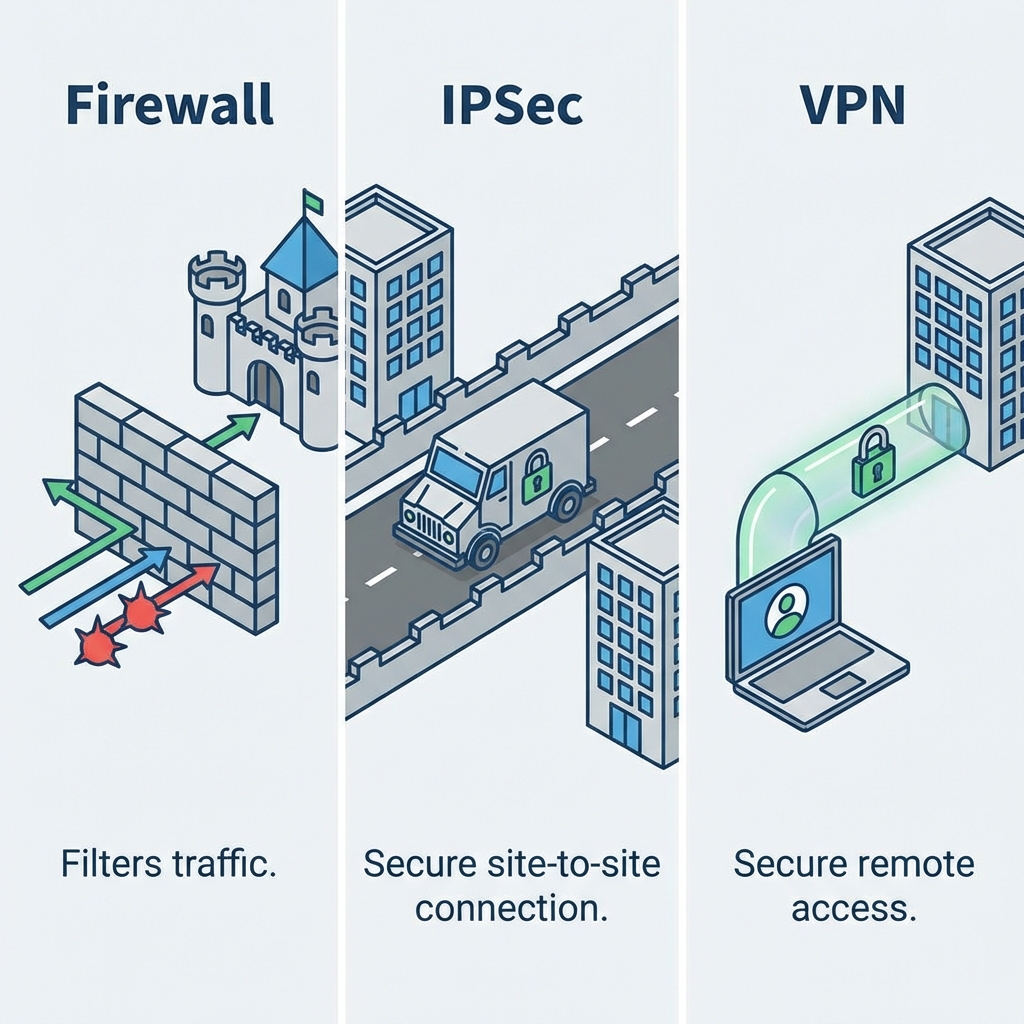
Firewall vs. IPSec vs. VPN: A Business View
Firewall 🛡️
Role: Perimeter Security
Business Use: The first line of defense for the entire company network. Protects all departments' servers and data from external attacks.
IPSec 🚚
Role: Data-in-Transit Security (Site-to-Site)
Business Use: Securely connecting fixed locations like Head Office to a Factory or a Data Center.
VPN 💻
Role: Secure Remote Access
Business Use: Enabling individual employees (remote workers, sales teams) to securely connect to the company network from anywhere.
Comparison: Three Layers of Security
Summary & Key Takeaways
- 🛡️ Firewalls are the essential first line of defense, protecting the digital assets of every business department.
- 🚚 IPSec secures the data "highways" between your business locations, crucial for integrated operations and finance.
- 💻 VPNs provide the flexible, secure access needed for a modern, mobile, and remote workforce, boosting productivity.
-
Network security is not just an IT cost; it's a strategic business investment that protects revenue, reputation, and enables new ways of working.
Thank You
Any questions?
Next Topic: Introduction to Databases and Business Data