Unit 3: Computer Software
Application Software and Industry Applications
ICT 110: IT for Business
Today's Learning Objectives
- ✅ Differentiate between system software and the various types of application software.
- ✅ Identify key software applications used in Finance, HR, Operations, and Marketing.
- ✅ Explain the role of integrated enterprise systems like ERP and CRM.
- ✅ Evaluate the critical factors for selecting the right software for a business.
Recap: Two Worlds of Software
System Software
The foundation. Manages computer hardware and provides a platform for applications to run.
- Operating Systems (Windows, macOS)
- Utility Programs (Antivirus, File Managers)
Application Software
The tools. Programs designed for end-users to accomplish specific tasks.
- Productivity Suites (MS Office)
- Business-Specific Software (Accounting, CRM)
Categories of Application Software
General-Purpose Applications
Versatile tools used across many industries and roles for common tasks.
e.g., Word Processors, Spreadsheets, Web Browsers, Presentation Software
Specialized / Business Applications
Tailored software designed for a specific business function or industry need.
e.g., Accounting Software, Inventory Management, Project Management Tools
Productivity Suites: The Business Standard
These general-purpose tools are essential for day-to-day operations in every department.
📊 Spreadsheets
(Excel, Google Sheets)
For financial modeling, budgeting, sales tracking, and data analysis.
💼 Word Processing
(Word, Google Docs)
For creating reports, contracts, marketing copy, and internal memos.
🎤 Presentation Software
(PowerPoint, Google Slides)
For sales pitches, team training, and reporting to stakeholders.
Beyond Productivity: Software for Core Business Functions
Every department relies on specialized software to manage its unique processes and data.
- 💰 Finance & Accounting
- 🤝 Human Resources
- ⚙️ Operations & Supply Chain
- 🎯 Marketing & Sales
Software in Finance & Accounting 💰
Core Functions
- Automating bookkeeping & invoicing
- Managing payroll and expenses
- Generating financial statements (P&L, Balance Sheet)
- Ensuring tax compliance
Example Applications
- Accounting: TallyPrime, QuickBooks, Zoho Books
- Financial Analysis: Microsoft Excel (Advanced), Power BI
- Auditing: Specialized audit management software
Software in Human Resources 🤝
Core Functions
- Managing the employee lifecycle (hire to retire)
- Streamlining recruitment (Applicant Tracking)
- Administering payroll and benefits
- Tracking performance and training
Example Applications
- HRIS: PeopleSoft, Workday, local solutions
- Recruitment (ATS): MeroJob, LinkedIn Recruiter
- Performance Management: Lattice, 15Five
Software in Operations & Supply Chain ⚙️
Core Functions
- Managing inventory levels
- Planning and scheduling production
- Coordinating logistics and distribution
- Overseeing project timelines and resources
Example Applications
- Inventory Management: Zoho Inventory, Odoo
- Project Management: Trello, Asana, Jira
- Supply Chain (SCM): SAP SCM, Oracle SCM
Software in Marketing & Sales 🎯
Core Functions
- Managing customer data and interactions
- Tracking sales leads and pipeline
- Analyzing customer behavior and campaign performance
- Automating customer communication
Example Applications
- CRM: Salesforce, HubSpot, Zoho CRM
- Data Analytics: Google Analytics, Power BI
- Email Marketing: Mailchimp, Sendinblue
Integrating It All: Enterprise Systems
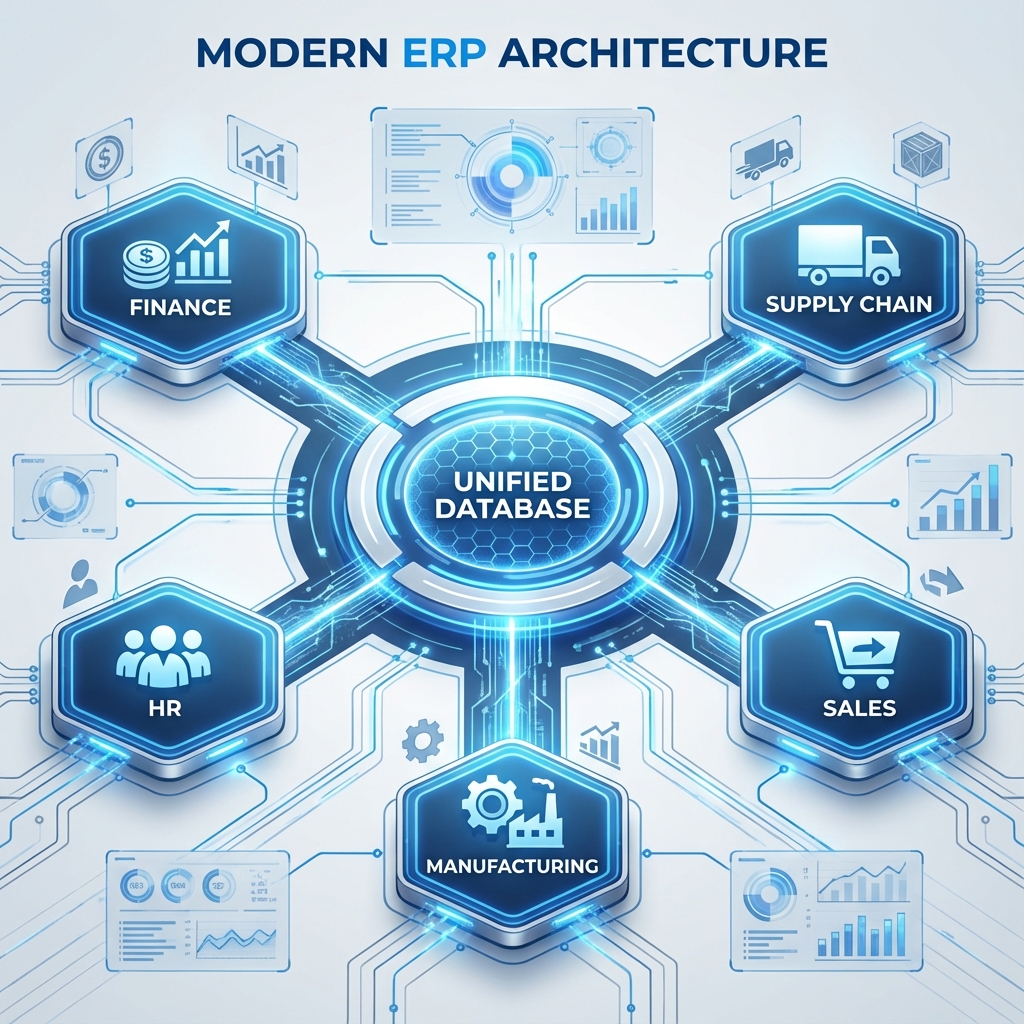
An ERP system connects all departments, allowing data to flow seamlessly between them.
Choosing the Right Software: A Strategic Decision
Scenario: A growing Nepali retail chain needs new inventory software. What should they consider?
- 🔍 Functionality: Does it handle multi-location stock? Does it integrate with our billing system?
- 💰 Cost (TCO): Beyond the license fee, what are the costs for training, support, and future upgrades?
- 🧩 Integration: Can it connect with our existing accounting software (e.g., Tally)?
- 📈 Scalability: Can the software support us when we expand from 5 to 25 stores?
- 🤝 Vendor Support: Is there reliable local support available in Nepal for implementation and troubleshooting?
- ⚖️ Licensing Model: Is a one-time purchase (On-Premise) or a monthly subscription (SaaS/Cloud) better for our cash flow?
Application Software in the Nepali Context
FinTech & Payments

eSewa, Khalti
These platforms are application software that enables digital payments, simplifying transactions for millions of users and thousands of businesses.
E-commerce & Logistics

Daraz
Uses a complex web of software for its website (customer interface), inventory management, CRM, and logistics coordination.
Manufacturing & FMCG

Chaudhary Group (CG)
Relies on large-scale ERP systems to manage its vast supply chain, production planning, distribution, and financials across diverse business units.
Key Takeaways
- ⚡ Application software translates business needs into computational tasks, driving productivity and efficiency.
- 💼 Every core business function—Finance, HR, Operations, and Marketing—relies on specialized software to operate effectively.
- 📊 Enterprise systems like ERP and CRM are crucial for integrating these functions and providing a unified view of the organization.
- 🎯 Selecting software is a strategic business decision that impacts cost, efficiency, and future growth. It's not just an "IT problem."