Deck 01
Role and Importance of IT in Modern Businesses
ICT 110: IT for Business
Learning Objectives
- ✅ Explain how Information Technology acts as a strategic asset across all business functions.
- ✅ Differentiate between IT's role in improving efficiency, enhancing effectiveness, and enabling innovation.
- ✅ Identify specific IT applications in Finance, Operations, HR, and Marketing.
- ✅ Analyze the impact of IT on business models using real-world examples from Nepal.
What is "IT" in a Business Context?
Information Technology (IT) is the use of computers, storage, networking, and other physical devices and infrastructure to create, process, store, secure, and exchange all forms of electronic data.
In business, it's not just about computers. It's the central nervous system that connects all parts of the organization.
IT's Core Roles: The Three Pillars of Value
⚙️ Operational Efficiency
Doing things faster and at a lower cost.
- Automating repetitive tasks
- Streamlining workflows
- Reducing errors
🎯 Business Effectiveness
Doing the right things to achieve goals.
- Better decision-making
- Improved customer service
- Enhanced communication
⚡ Strategic Innovation
Doing new things to gain a competitive edge.
- Creating new products/services
- Entering new markets
- Transforming business models
IT Across Functions (1/2)
💰 In Finance & Accounting
- ERP Systems (e.g., SAP, Oracle): Integrate financial data across the entire company.
- Accounting Software (e.g., Tally): Automates bookkeeping, invoicing, and financial reporting.
- Budgeting & Forecasting Tools: Use historical data to predict future financial performance.
- FinTech Solutions: Digital payments, online lending platforms.
⚙️ In Operations & Supply Chain
- Supply Chain Management (SCM) Systems: Track goods from supplier to customer.
- Inventory Management Systems: Optimize stock levels, prevent shortages.
- Project Management Software (e.g., Jira, Asana): Plan, execute, and monitor projects.
- Quality Control Systems: Use sensors and data to ensure product quality.
IT Across Functions (2/2)
🤝 In Human Resources (HR)
- Human Resource Information Systems (HRIS): Central database for all employee information.
- Payroll Systems: Automate salary calculation and disbursement.
- Applicant Tracking Systems (ATS): Streamline recruitment and hiring.
- E-Learning Platforms: Provide online training and development for staff.
📊 In Marketing & Sales
- Customer Relationship Management (CRM) Systems: Manage all customer interactions and data.
- Data Analytics Tools: Analyze customer behavior to personalize marketing.
- Sales Force Automation: Equip sales teams with tools to manage leads and close deals.
- E-commerce Platforms: Enable online sales and transactions.
The Glue: Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP)
ERP systems integrate all core business processes into a single, unified system.
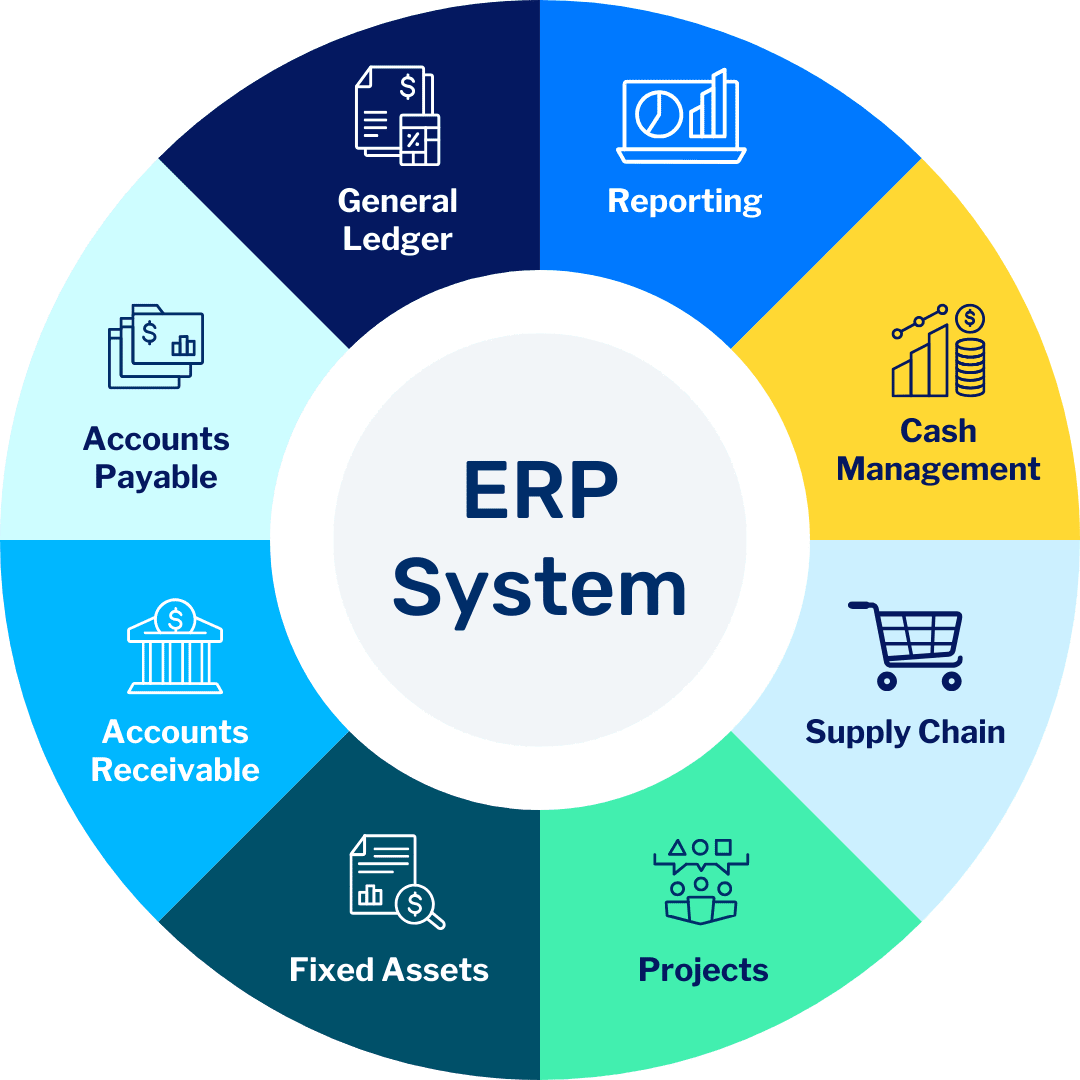
🔍 IT for Strategic Decision-Making
How do managers make informed choices? Through data.
Business Intelligence (BI) & Analytics: Technologies and practices for the collection, integration, analysis, and presentation of business information.
- Dashboards: Visual displays of key business metrics (KPIs) in real-time.
- Data Warehousing: Storing vast amounts of historical data for analysis.
- Predictive Analytics: Using data to forecast future trends, such as customer churn or sales demand.
Example: A Manager's Dashboard
A retail manager might use a BI dashboard to answer critical questions instantly, without waiting for manual reports.
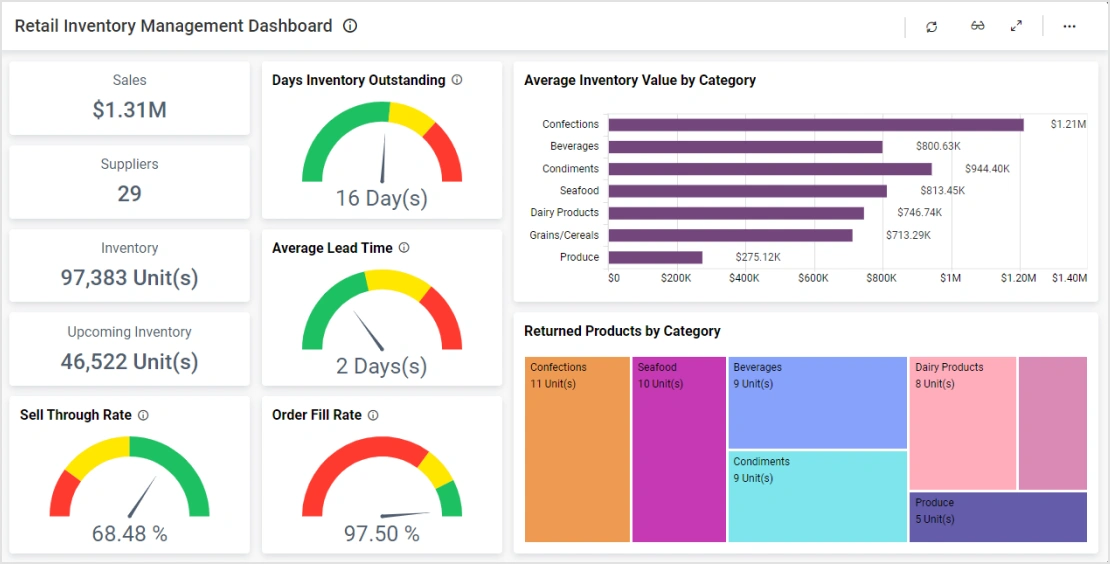
This single screen combines data from Sales (CRM), Inventory (SCM), and Finance (ERP).
Digital Transformation: Beyond Automation
This is not just about digitizing old processes. It's about fundamentally rethinking the business model.
Before IT Transformation
- Physical bank branches
- Paper-based records
- Manual inventory checks
- In-person meetings
After IT Transformation
- Mobile banking apps
- Cloud-based data (ERP/CRM)
- Real-time supply chain tracking
- Global video conferencing
Digital transformation leverages IT to create new sources of value and customer experiences.
Activity: Match the Tool to the Goal
For each business goal, which IT system provides the most direct support?
Business Goal
- Reduce time-to-hire for new employees.
- Improve on-time delivery of products.
- Get a single view of all customer interactions.
IT System
- A) Supply Chain Management (SCM)
- B) Customer Relationship Management (CRM)
- C) Applicant Tracking System (ATS)
Answers: 1-C, 2-A, 3-B
💼 IT in Practice: The Nepali Context 🇳🇵
eSewa (FinTech)
Function: Finance
Impact: Transformed payments from cash-based to digital. Enables peer-to-peer transfers, utility payments, and merchant services, creating a new digital economy.
Daraz (E-commerce)
Function: Operations & Sales
Impact: Uses sophisticated SCM and logistics IT to manage thousands of sellers and deliver nationwide. CRM and analytics drive personalized marketing.
CG Foods (Manufacturing)
Function: Operations & Finance
Impact: Employs ERP systems to manage production, inventory, and distribution of products like Wai Wai across a global supply chain, ensuring efficiency and quality.
Summary: Key Takeaways
- ✅ IT is a strategic asset, not just a technical function. It must be aligned with business goals.
- ✅ IT drives value by improving efficiency (cost/speed), effectiveness (decision-making), and enabling innovation (new models).
- ✅ Every business function—Finance, Operations, HR, Marketing—relies on specialized IT systems to perform its role.
- ✅ Enterprise systems like ERP are crucial for integrating data and processes across the entire organization.
Thank You!
Any questions?
Next Topic: Key IT Trends Transforming Businesses